Where is the fear? And how can love diffuse it? These are the questions inherent in almost all motivational challenges. By developing a deeper understanding of the fundamental relationship of love and fear and how they function in the human organism, we learn to graciously navigate emotionally charged thought processes and volatile perceptual boundaries, thus inviting profound shifts of perspective in real time.
The Primal Elements
Love and fear are elemental forces we are born with and experience throughout our lifetimes, yet they defy absolute comprehension. Behavioral philosophies and psychological theories of the mind commonly consider love and fear as the primary emotions of the reptilian brain, with all other emotions being secondary. Physiologically, love and fear are tied to our survival instinct and the release of the stress (fear) hormones adrenaline and cortisol, and their anti-stress (love) hormonal counterpart, oxytocin. On a mental, emotional and physical basis, love connects us—within ourselves, to each other, and to the world around us—while fear separates us.
Consequently, love and fear are also the primal factors of motivation. Love is the impetus for connecting to our world so that we develop and thrive, while fear compels separation as a means of protection for ourselves and our loved ones. Comprehending this innate relationship of love and fear as the motivational foundation of human behavior offers a tangible context for resolving conflict and inspiring transformation, both individually and collectively.
In our innovative programs and practices at Cathexis Therapeutic Imagery, we actively enjoin our clients in the mindful process of identifying separating behavior (fearful actions and/or reactions based on perceived threats) and responding with connecting behavior (caring gestures and acts of compassion). This serves as an effective strategy for breaking down complex issues into workable pieces that can be addressed in the moment, and empowers change as individuals, teams and organizations realize how compassion is the potent connective tissue in their internal and external relationships. We call this dynamic cognitive empathy, which is an important component of a larger skill-set known as emotional intelligence.
Excavating Maslow’s Pyramid
Any credible discussion of the psychology of motivation requires consideration of Abraham Maslow and his motivational theory based on human needs. So let’s examine Maslow’s infamous hierarchy of needs, which is archetypically depicted as levels within a pyramid.
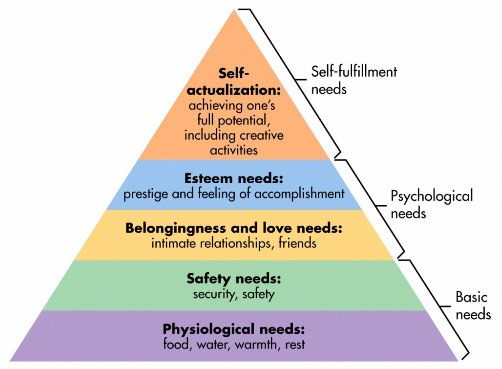
Abraham Maslow’s Hierarchy Of Needs Is More About Self-Actualization Than Motivation
Maslow proposed his hierarchy of needs in a paper entitled “A Theory of Human Motivation,” which was published in 1943. The concepts have provided a framework for the psychology of motivation and have been widely utilized to conceptualize policy and practice in the social sciences and in business. The precept is that human behavior is motivated by the satisfaction or frustration of needs, which are arranged in a predominant hierarchy from physiological, to safety, to social, to esteem, to self-actualization.
Yet Maslow’s theory has its share of criticisms, the most significant of which are the limited scope of his research sample and the subjective methodology used in formulating the characteristics of “self-actualization.” The study was conducted by analyzing the biographies and writings of eighteen people, most of whom were highly educated white males. The subjects included Albert Einstein, Thomas Jefferson, Abraham Lincoln, William James, Aldous Huxley, Gandhi, and Beethoven, as well as students from the top 1% of college populations. Although the study did include extraordinary women like Eleanor Roosevelt and Mother Teresa, they comprised a small percentage of his sample. Thus, the validity of Maslow’s theory is questionable as to females, as well as individuals from lower social classes and varying ethnicities. It is also relevant to note that Maslow did not include children in his study.
The empirical and theoretical criticisms of Maslow’s hierarchy of needs contemplate the following:
- Cultural relativity and universalism
- The validity and ordering of the original categories of needs
- The lack of defined and measured variables throughout the model
Contemporary research by Tay & Diener (2011) tested Maslow’s theory by analyzing the data of 60,865 participants from 123 countries, representing every major region of the world. The survey was conducted from 2005 to 2010. The results of the study support the view that universal human needs appear to exist regardless of cultural differences. However, the ordering of the needs within the hierarchy was incorrect (see SimplyPsychology.org article here). While this and other research refute the existence of the original need categories and question the directional hierarchy that Maslow proposed, these studies do support the existence of lower and higher level needs, along with gratification and deprivation as motivators of self-actualization.

“None of Maslow’s needs can be met without social connection.” ~ Pamela Rutledge, Ph.D., M.B.A.
In her astute Psychology Today article: ‘Social Networks, What Maslow Misses,’ Dr. Pamela Rutledge takes issue with the widespread assumption represented by the pyramid: that human connection is NOT a primary need or instinct, but occurs instead as an upward climb from food and shelter. She points out the collaborative effort required for basic hunting, gathering and protection from the elements, and illuminates how the drivers of social connection are intimately interwoven into our basic survival, even in a world shifting with technology.
Purely on the basis of definition, a persuasive argument exists that motivation and self-actualization are not one in the same. And, as you can see, a rigorous unearthing of Maslow’s pyramid uncovers a framework that is clearly about self-actualization—the process of systematically meeting human needs. In fact, one might even conclude that a better title for Maslow’s 1943 paper would have been “A Theory Of Human Self-Actualization.”
Our Wonder Years
A rational mind would consider food, water and shelter more urgent requirements than affection and nurturing. The mature individual would deem safety a priority over compassionate interaction. And pragmatic adults would agree that security in maintaining these basic necessities is more important than self-esteem and the sense of belonging.
Yet as infants, wrapped in swaddling clothes and safely cuddled in loving arms, nursing at our mother’s breast and having all our fundamental needs met for us, the opposites all hold true. Common sense, supported by thousands of research studies on childhood development, tells us that at this stage of life, when sentience is rapidly developing both psychologically and physiologically, love and esteem needs are primary—not a third or fourth tier priority.

As infants and children, we acquire our vast repertoire of skills by studying the faces, voices and actions of others, beginning with our parents and primary caregivers.
The importance of early childhood development has been acknowledged by economists, behavioral scientists, educators, neuroscientists and biologists. Our formative years effect how we grow and develop through adolescence and into adult life. The most powerful external influence on all aspects of our development, resilience and adaptability to life’s challenges, is the quality of love we receive from our parents and primary caregivers.
Our formative attachment relationships determine our physiological functioning, cognitive perception and emotional awareness, development of language skills, and understanding of ourselves, others, and the unfolding world around us. The varying forms of separation anxiety experienced by all children, which can endure or recur throughout childhood, demonstrate both our innate understanding of the need for love, and our instinctive fear at the prospect of being separated from those who provide it to us.
The fundamental physiological need for emotional interaction with those who love and care for us is how motivation awakens in our lives. Love drives our desire to connect, learn and develop. When circumstances challenge our bonds to these relationships, we sometimes experience fearful reactions that we must learn to cope with. When these critical attachment relationships are non-existent or nominal, or if they are significantly compromised or severed during our childhood journey, traumatic developmental, emotional and psycho-social consequences can result—all of which are rooted in a deep and abiding fear of not receiving the love we need.
Connecting Or Separating?
Motivation is a quickening of inner awareness and self-possession based upon two factors: the drive to fulfill our basic need for love and all that we associate with it, and the experience of fear—the circumstances, situations and people we perceive as threats to that love, or to our own safety and survival. Cognition, curiosity, comprehension, exploration, discovery, affection, and affinity are among the developmental aspects of our formative years, and are all connecting behaviors primarily associated with love. Apprehension, worry, indecision, anger, aggression and aloofness are among the common childhood separating behaviors associated with fear.
Yet the primary emotions of love and fear are also conceptual in nature and as we learn more about how they influence our world, we manifest additional behaviors that reflect the broader spectrum of secondary emotions related to them. This brief Slideshare illustrates how love and fear function as powerful forces of motivation in our everyday lives, and reminds us that we can alter our perspective by being mindful and choosing compassion and empathy.
Our lives are filled with transition. Events both expected and unexpected impact our day to day functioning, self-esteem and sense of purpose. Growth and adaptation in a fluid and fast-paced world of technological, economic, political and personal challenges are prerequisites to our health, happiness and survival. The catalyst in how we respond to the trials and tribulations posed by these largely externalized factors, is motivation—an internalized, somatic phenomenon that is greatly influenced by our developmental associations with love and fear—and which, throughout life, continues to be shaped and impelled by our social interactions.
“Motivation kinetically embodies the desires, ambitions, revelations and trepidations that both consciously and subconsciously order our lives.”
Understanding the intrinsic relationship of love and fear helps us identify the underlying motivational factors in ourselves and others. We recognize separating behaviors that result from falsely perceived threats, and distinguish them from comportment rooted in deeper-seated fears. We also embrace the unifying force of love. By mindfully connecting with caring gestures, acts of kindness and compassion, and critical attending, we discover that fearful reactions can be mitigated and diffused. This is how practicing cognitive empathy negates the limiting aspects of fear and inspires us to address larger connective issues and fulfill needs that ultimately define actualized people—individually, collectively and organizationally.
©2016 Shawn Quinlivan, C.Ht. & Cathexis Therapeutic Imagery. All Rights Reserved.
 Cathexis Therapeutic Imagery specializes in innovative approaches to workplace wellness, mindfulness training, and personal development. Via private coaching, presentations, workshops, training events, and our partnership in the unique online wellness community Your Wellness Room—used by Kaiser Permanente, EFactor and other notable companies—our nationally recognized programs and practices help people and organizations make positive changes. Please call for a free consultation at (818) 512-4371 or contact us via email.
Cathexis Therapeutic Imagery specializes in innovative approaches to workplace wellness, mindfulness training, and personal development. Via private coaching, presentations, workshops, training events, and our partnership in the unique online wellness community Your Wellness Room—used by Kaiser Permanente, EFactor and other notable companies—our nationally recognized programs and practices help people and organizations make positive changes. Please call for a free consultation at (818) 512-4371 or contact us via email.
 Cathexis Therapeutic Imagery specializes in innovative approaches to workplace wellness, mindfulness training, and personal development. Via private coaching, presentations, workshops, training events, and our partnership in the unique online wellness community Your Wellness Room—used by Kaiser Permanente, EFactor and other notable companies—our nationally recognized programs and practices help people and organizations make positive changes. Please call for a free consultation at (818) 512-4371 or contact us via email.
Cathexis Therapeutic Imagery specializes in innovative approaches to workplace wellness, mindfulness training, and personal development. Via private coaching, presentations, workshops, training events, and our partnership in the unique online wellness community Your Wellness Room—used by Kaiser Permanente, EFactor and other notable companies—our nationally recognized programs and practices help people and organizations make positive changes. Please call for a free consultation at (818) 512-4371 or contact us via email.





